
RecognizingInterstitial VersusAirspace Disease
© William Herring, MD, FACR

Why learn the difference?
Many times these patterns overlap
But frequently, recognition of oneor the other helps with the…
Differential diagnosis

Parenchymal Lung Disease
Two Major Types
Alveolar (air space)
Interstitial

Airspace Disease
Soft-tissue opacities
With hazy and indistinct margins
Tend to respect segmental orlobar boundaries
May contain air bronchograms

Air Bronchogram
Bronchi usually not visible
Walls are thin, they contain air, are surroundedby air
When something of fluid density fillsalveoli, air in bronchus becomes visible
Pulmonary edema fluid
Blood
Gastric aspirate
Inflammatory exudate

Air Bronchogram
The visibility of air in the bronchi becauseof surrounding airspace disease is calledan “air bronchogram”
An air bronchogram is most often a sign ofairspace disease

The black branchingstructures are theresult of air in thebronchi, now visiblebecause densityother than airsurrounds them (inthis case it isinflammatory exudatefrom a pneumonia).

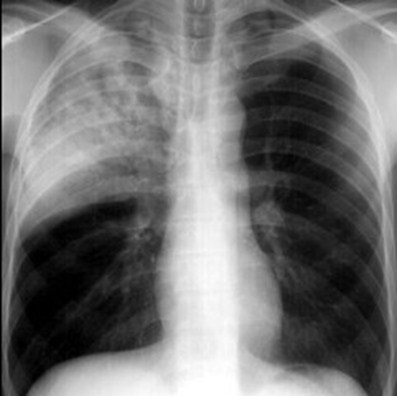
Pulmonary edema
This disease isfluffy and indistinctin its margins, it isconfluent andtends to behomogeneous. Inboth upper lobes,you can see airbronchograms.This is an alveolar(airspace) disease,in this casepulmonary edemaon a non-cardiogenic basis.

Common Airspace Diseases
Pneumonia – inflammatory exudate
Pulmonary edema – edema fluid
Pulmonary hemorrhage – blood
Aspiration – gastric juices

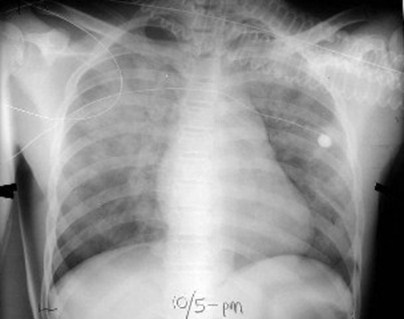
Aspiration pneumonia at both bases
Airspace Disease
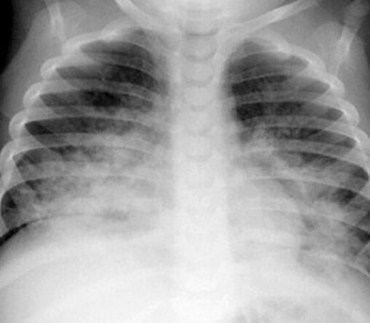

Interstitial Lung Disease
Now referred to as infiltrative lung disease
Discrete particles of disease
Inhomogeneous
Doesn’t respect lobar boundaries
Usually no air bronchograms
Made up of lines (reticular) or dots(nodular) or both (reticulonodular)

Interstitial disease – discrete,inhomogeneous, no airbronchograms
Airspace disease – fluffy,indistinct, homogeneous,contains air bronchograms
Interstitial versus Airspace Disease
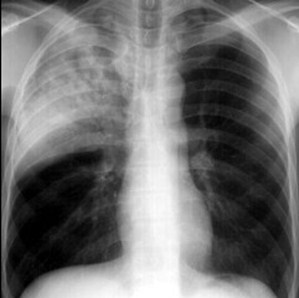

Common Interstitial Lung Diseases
Cancer – primary or metastatic
Sarcoidosis
Cystic fibrosis
Asbestosis

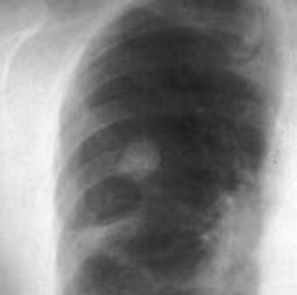
Right upper lobe mass isa bronchogeniccarcinoma. It is sharplymarginated, relativelydiscrete, contains no airbronchograms. It beganin the interstitium of thelung.
Bronchogenic carcinoma – large cell

Interstitial DiseasesExamples of mostly nodular patterns
Hematogenously disseminatedmetastatic disease, e.g. renal cell ca
Silicosis
Miliary tuberculosis

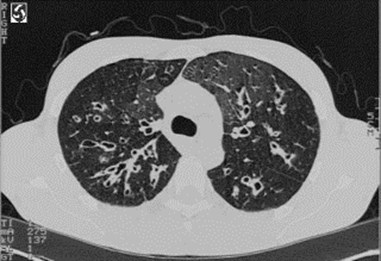
This CT of thechest showsthickenedbronchial wallswith extensivedilatation of thebronchi (bronchishould besmaller thantheiraccompanyingblood vessel).This interstitialdisease is CysticFibrosis.
Cystic Fibrosis

This is a diffuseinfiltrative(interstitial)disease that iscomposedprimarily of lines(reticular disease).Examples ofmostly reticulardisease includePneumocystispneumonia andeosinophilicgranuloma.
Pneumocystis Pneumonia

Eosinophilic granuloma of the lung
Pulmonary interstitial edema
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Rheumatoid lung
Interstitial DiseasesExamples of mostly reticular patterns

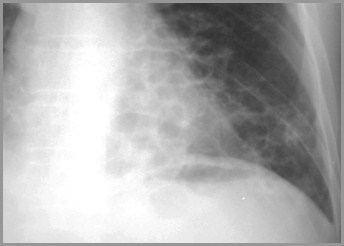
Interstitial lung diseasewith coarse, criss-crossing pattern iscalled “honeycomb”pattern. It is seen insuch diseases aseosinophilicgranuloma of the lungand bronchiectasis.
Bronchiectasis

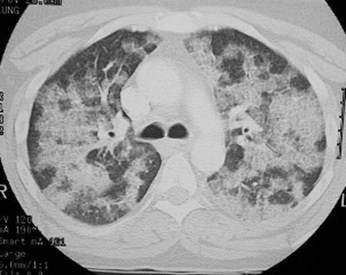
Another diffuseinfiltrative patternIn the lung is“ground-glass”opacification, seenon CT. Thoughnon-specific, it isdifferentiated fromairspace diseasein that airbronchograms arenot present andthe blood vesselsare usually stillvisible through thedisease.
Alveolar proteinosis

Take Home Points
Though somewhat artificial, lungdisease can be divided into airspace andinterstitial (infiltrative) patterns
Airspace dz is fluffy, confluent with airbronchograms
Interstitial dz is diffuse, discrete, tendsto occur in lines, dots or a combinationof the two



Which of the following isairspace disease orinterstitial lung disease?
Answer follows on slide after question
Quiz

Airspace or interstitial?
Answer follows on next slide
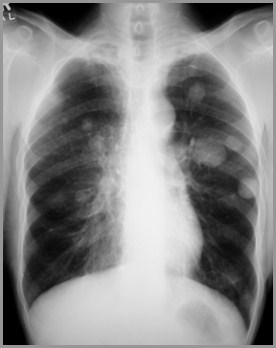

This is interstitial disease
There are multiplediscrete nodules inboth lungs. They arewell-defined, do nothave air bronchogramsand do not respectlobar boundaries.These are metastasesfrom a colon cancer.
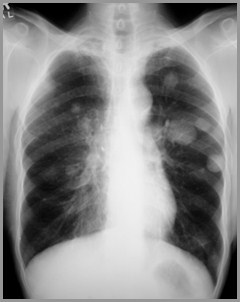

Answer follows on next slide
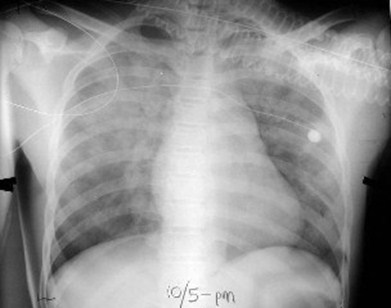
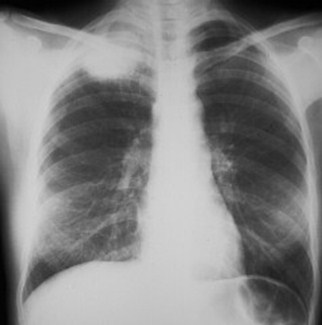
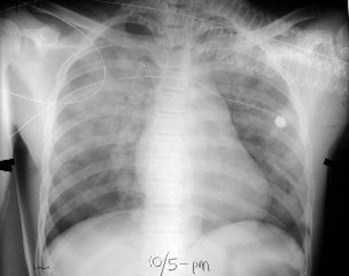
Airspace or interstitial?

There is diffuseairspace (alveolar)disease which hassomewhat of a “bat-wing” appearance.The disease is fluffy,confluent and is notmade up of discretelines or dots. This isCHF.
This is airspace disease

Answer follows on next slide
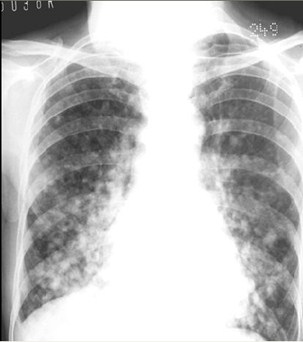
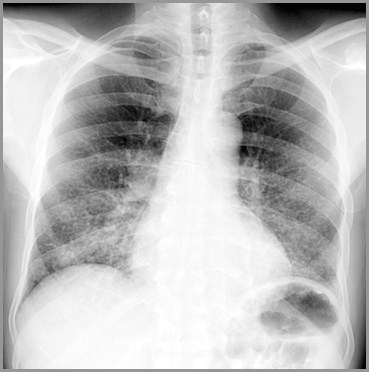
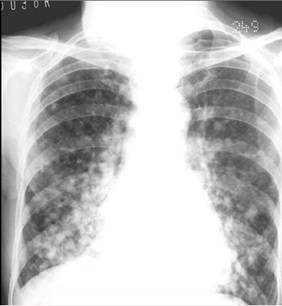
Airspace or interstitial?

There are multiplenodules in both lungsfrom metastaticdisease of breastprimary. The diseaseoccurs in a discretenodular pattern with noair bronchograms.
This is interstitial disease

Answer follows on next slide
Airspace or interstitial?
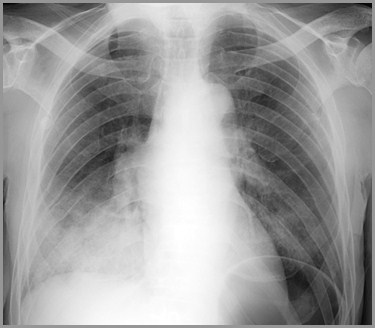

This is localizedairspace disease. Itis lobar andsegmental indistribution, isconfluent, hasindistinct margins. Itis pneumonia of theright lower lobe.
This is airspace disease


Congratulations, You Graduate

I know anairspacediseasewhen Isee oneI know anairspacediseasewhen Isee one
To return to the beginning of this module, Click HereTo return to the beginning of the quiz, Click Here